Is there such a thing as Ear Ache Drops, Covid Ache Ear, Ear Aches, or Ear Pains will this help you? Do you know that you don’t hear? From the Ear. A lot of times you can hear things that are in your imagination. People hear noises all the time that are not necessarily picked up by your eardrum but could be from your mind your mindset is everything. your hearing is everything

A demonstration of this is when people say they can hear their heartbeat in their ears this is a common sign of high blood pressure
One ear infection can happen plus also double ear infections can be common too. This can also influence your sinuses. Which can also give you a sore throat and ear pain at the same time!

Cold and flue can set this off, especially if you have low immunity or when receiving vaccines you can also get pains in the ears some common symptoms such as with the current crisis most people have experienced was when having covid you could get Covid ear infection and when having flue or cold viruses you can get sudden ear pain, fungal ear infection.

Have you ever heard of the term – TMJ symptoms ear what is this? Have you got this right now?
(TMJ) a syndrome is a pain in the jaw joint that can be caused by a variety of medical problems. The TMJ connects the lower jaw to the skull in front of the ear. Certain facial muscles that control chewing are also attached to the lower jaw. Which can also give you sudden ear pain!

What’s your Ear all about?
Your ear has three main features: outer, middle, and inner. You use all of them in hearing. Audio sound comes in through your outer ear. They reach your middle ear, where they make your eardrum create a vibration.
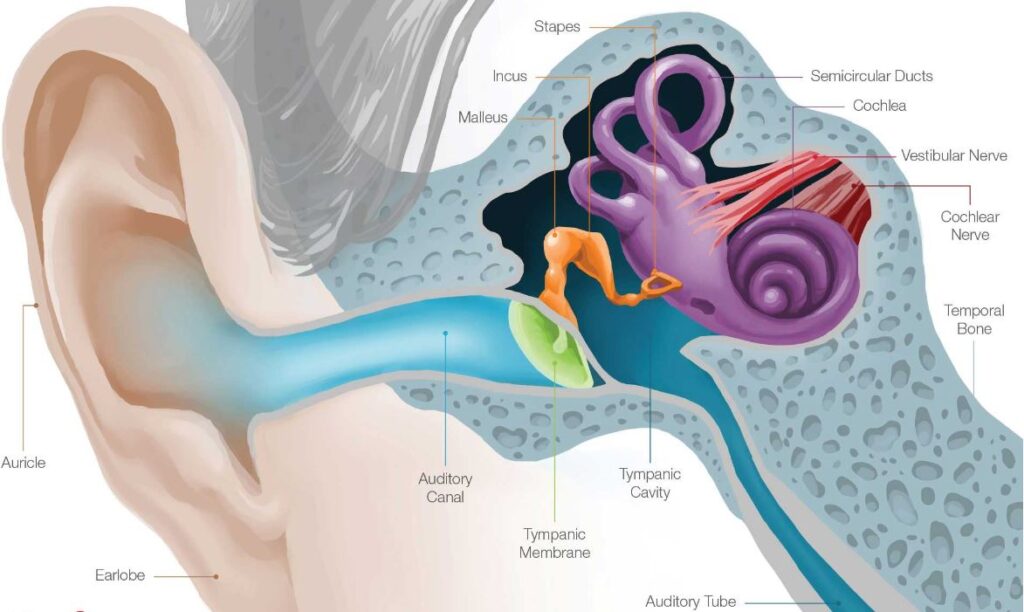
Outer Ear
auricle (cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head)
auditory canal (also called the ear canal)
eardrum outer layer (also called the tympanic membrane)
The outer part of the ear collects sound. Sound travels through the auricle and the auditory canal, a short tube that ends at the eardrum.
Middle Ear
has a cavity which is also called the tympanic cavit
has ossicles which is 3 tiny bones that are attached
has a malleus or can be named a hammer which looks like a long handle attached to the eardrum
includes a incus or could be named as the bridge bone between the malleus and the stapes
stapes are can be named as a stirrup or also know as the footplate; the smallest bone in the body
The Inner Ear
finally the inner ear includes has a oval window – connects the middle ear with the inner ear
has semicircular ducts – filled with fluid; attached to cochlea and nerves; send information on balance and head position to the brain
includes the spiral cochlea – spiral-shaped organ of hearing; transforms sound into signals that get sent to the brain
includes unique auditory tube – drains fluid from the middle ear into the throat behind the nose
The vibrations are transmitted through three tiny bone structures, called ossicles, in your middle ear. The vibrations travel to your inner ear, a funny-looking snail organ. The inner ear makes the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain. Your brain recognizes them as sounds. The inner ear also controls balance with a special chemical in the ear.
Are There other Ear Conditions

A variety of conditions may affect your hearing or put you off balance:
Ear infections are most common in infants and young children.
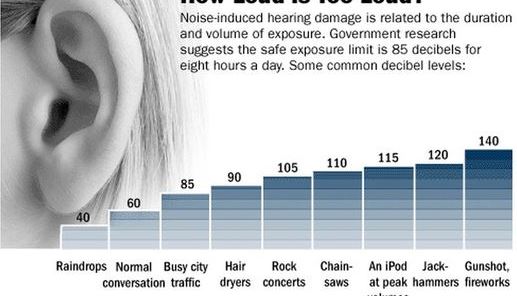
Tinnitus, a roaring in your ears, can be the result of loud and is, constant vibration in the ear.
Meniere’s disease may be the result of fluid problems in your inner ear; its symptoms include tinnitus and dizziness affect effect other parts of your face related to the ear.
Ear barotrauma is an injury to your ear because of changes in barometric (air) or water pressure. Deep divers are prone to this injury.
One of the most common questions asked by people with hear loss is?
Can hearing Loss be reversed.
Losing your hearing can be scary — sometimes a major one that makes you worry.
While some forms of hearing loss aren’t reversible, many are. But how does it affect you?
how to tell if hearing loss is permanent or temporary
Earwax Build-up: Reversible
Earwax helps clean and protect the ears. Normally, your ears will clear it out on their own.
If you use cotton swabs to clean them, you may be pushing the wax in deeper. This can make it gather and get stuck.
That’ll make it hard for you to hear.in fact, most doctors will tell you that the only thing you should put in your ear should be the size of your elbow and not penetrate the eardrum.
It’s not hard to treat that build-up and get your hearing back. Home treatments work well in most cases. Put a few drops of mineral oil or baby oil in the ear to help the wax work its way out can sometimes work wonders.
You can also buy drops at your nearest chemist that help soften ear wax. Avoid products with hydrogen peroxide if your ear canal is dry. Personally, natural ear remedies are key
See a doctor if home treatments don’t work or if you have diabetes. They can remove the wax safely with medical tools. Or they might flush it out with water or saline.
assymetric hearing loss what is it?
Simply put assymetric hearing loss is when you have ear loss in one ear and its greater or smaller in what you are hearing form one ear to the other.
low-frequency hearing loss what is this?
A low-frequency hearing loss is a hearing loss where you cannot hear sounds that occur in the lower end of the frequencies, which are transmitting frequencies of 2,000 Hz or lower. These frequencies are also called the deeper or low-pitched sounds.

It can be difficult to identify a low-frequency hearing loss. People with a low-frequency hearing loss are often still able to understand normal speech and to take part in conversations but may ask to repeat time to time.
However, a symptom could be difficult hearing conversation within groups of people or problems hearing well in noisy environments and in places with background noise. Another symptom can be that it is difficult to hear the bass sounds when listening to music.
low-frequency hearing loss what is this?
A low-frequency hearing loss is a hearing loss where you cannot hear sounds that occur in the lower end of the frequencies, which are transmitting frequencies of 2,000 Hz or lower. These frequencies are also called the deeper or low-pitched sounds.
what are the Causes of low-frequency hearing loss
some Causes of low-frequency hearing loss can be age, noise, diseases or infections. It may also be caused by genetic factors.
A low-frequency hearing loss is typically a sensorineural hearing loss, which is a hearing loss normally caused by damage to the hair cells in the inner ear that receive the sounds which converts them to signals that are transmitted to the brain by the auditory nerves.

If you have mid-range hearing loss, your audiogram will be shaped like a bell, or the letter U. This is also known as cookie-bite hearing loss.
“when doctors have examined a patient with this pattern of hearing loss has an audiogram and the hearing frequencies are graphed, the pattern is a ‘U’ that looks as if someone took a bite out of a cookie,”
according to the Dr. Jordan Glicksman, MD, MPH, FACS, FRCSC, an otolaryngologist, rhinologist and skull base surgeon, and a part-time lecturer at Harvard Medical School.
What have people tried to give comfort from this Click here for more info
